Analyzing discrete data
This analysis enables you to analyze numerical data. It creates a column analysis in which indicators, appropriate for numeric data, are assigned to the column by default.
Discrete data can only take particular values of potentially an infinite number of values. Continuous data is the opposite of discrete data, it is not restricted to defined separate values, but can occupy any value over a continuous range.
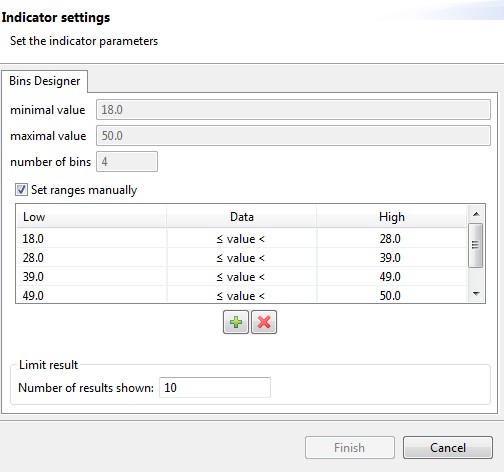
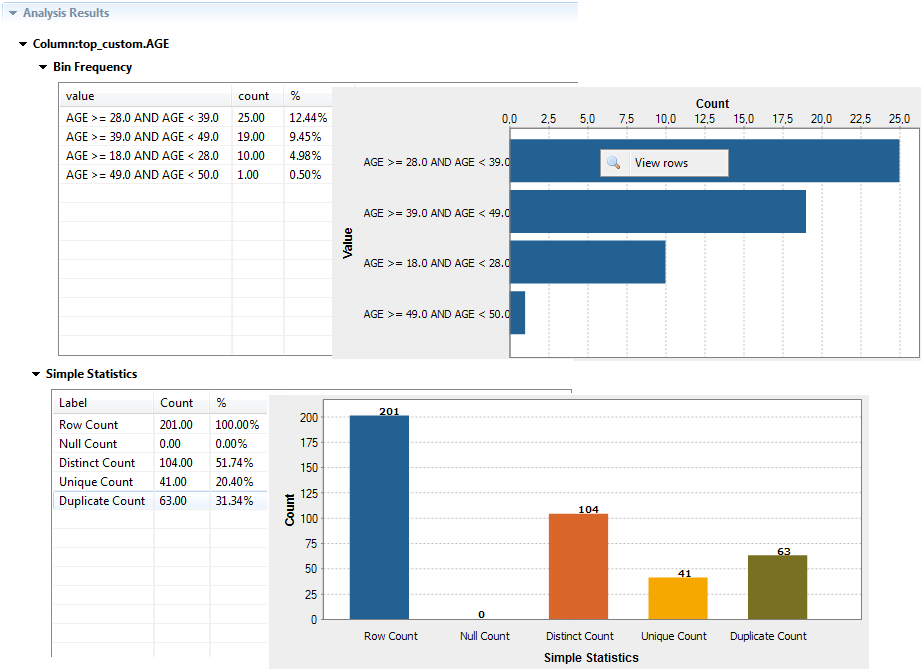
This analysis uses the Bin Frequency indicator that you must configure further in order to convert continuous data into discrete bins (ranges) according to your needs.