Building a Job as a Microservice (Spring-boot) for ESB Docker image
About this task
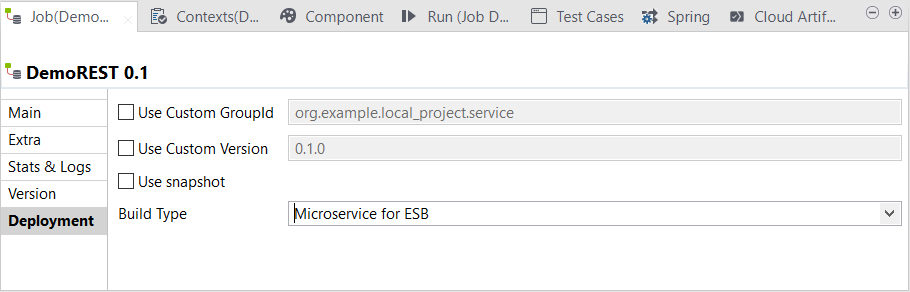
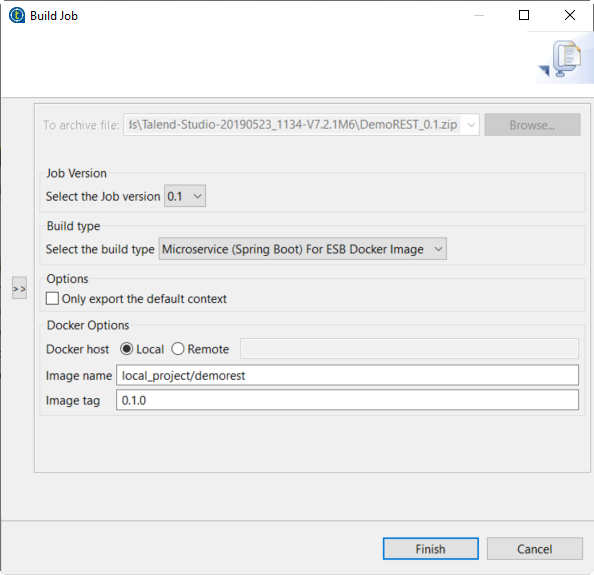
In the Build Job dialog box, you can build a Data Service Job as a
Microservice (Spring-boot) for ESB Docker image in order to execute it on a Docker
engine.
Information noteWarning: Only Jobs that include the tRESTRequest component can be built as a Spring-boot based ESB
Microservice Docker image.
Procedure
Results
Did this page help you?
If you find any issues with this page or its content – a typo, a missing step, or a technical error – let us know how we can improve!