Analyzing the heat map
The heat map helps you quickly see the importance of a feature and matching key in a model.
In the following examples, you will see how to analyze the heat map and, depending on the minimum model quality you want to obtain, how you can decide if a feature is necessary to the model.
- The site name,
- The address and
- The source of the previous data.
The database and the settings remained the same; only the matching keys changed.
First example: the site name is the matching key
In this example, one input data is set as a matching key.
The model quality is: 0.802. It is high, but not enough to have a reliable model.
In the following examples, more matching keys are set to see their impact on the model quality.
Second example: the address and site name are the matching keys
In this example, one matching key is added to the previous example.

The model quality is: 0.917. It is significantly higher than the previous example.
Adding a matching key helps you see that no features from the Site name input data are important.
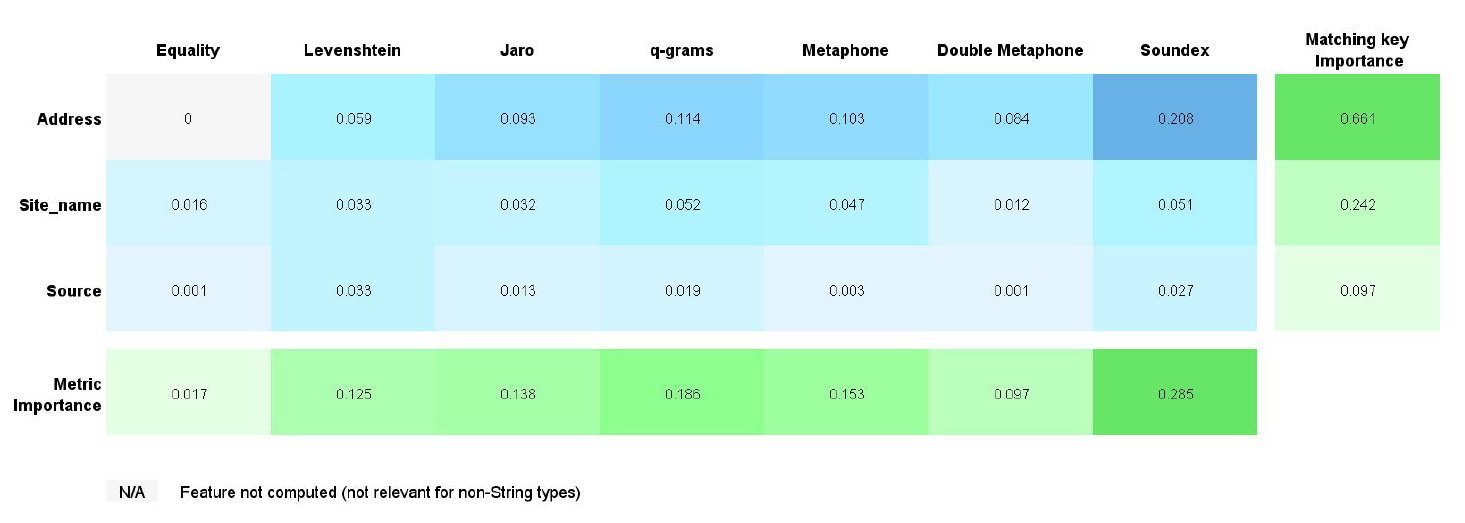
Third example: the address, site name and source are the matching keys
In this example, one matching key is added to the previous example.

The model quality is: 0.925.
You can see that no features from the Source input data are important. If you compare this example to the previous one, the model quality is higher but not enough to make this matching key essential to the model.
Summary
| Example | Matching keys | Model quality |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Site name | 0.802 |
| 2 | Address and Site name | 0.917 |
| 3 | Address, Site name and Source | 0.925 |
After setting different matching keys and running several Jobs, you can see that some features are not important to the model.
Even if a model quality is satisfying, you can add or remove matching keys to compare the results.
Depending on your database, a less important feature can be noise in the model.
Depending on the minimum model quality you want to obtain, you can decide if a matching key is necessary to the model.
Did this page help you?
If you find any issues with this page or its content – a typo, a missing step, or a technical error – let us know how we can improve!
